Vacuum Furnaces: Advanced Heat Treatment for Superior Material Properties
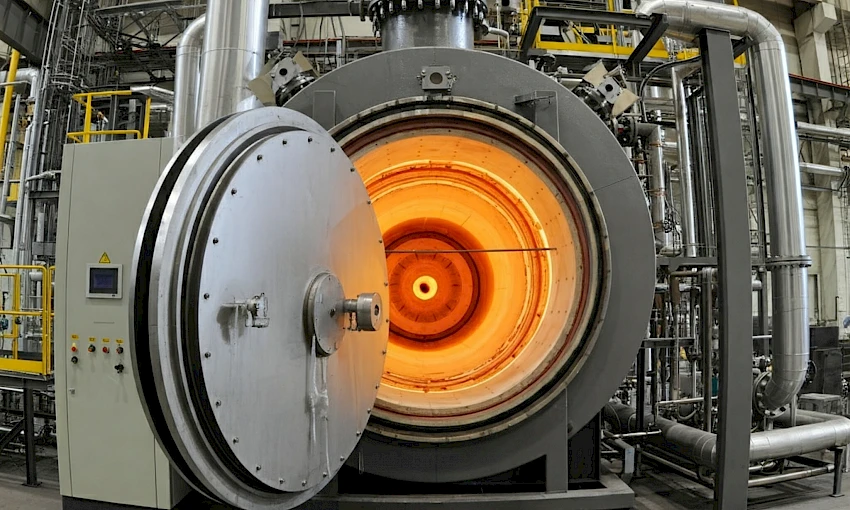
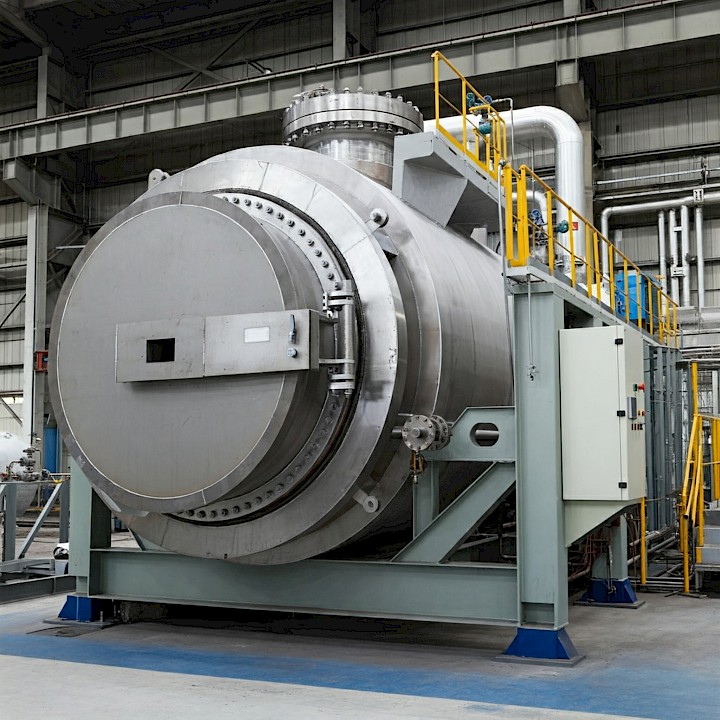
A vacuum furnace is a specialized industrial furnace that operates in a vacuum environment, meaning the air within the furnace chamber is removed to create a low-pressure environment. This unique environment offers significant advantages for various heat treatment processes.
What is a Vacuum Heat Treatment Furnace?
Vacuum heat treatment furnaces are specifically designed to perform a range of heat treatment processes on materials like metals, ceramics, and composites in a vacuum. These processes include:
-
Hardening: Increasing the hardness of a material by heating and rapid cooling.
-
Tempering: Reducing the brittleness of a hardened material while maintaining its strength.
-
Annealing: Softening a material to improve ductility and reduce internal stresses.
-
Brazing: Joining two or more materials using a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature.
-
Sintering: Forming a solid mass of material by heating without melting.
Key Components of a Vacuum Heat Treatment Furnace:
-
Heating Chamber: A well-insulated chamber where the workpiece is heated.
-
Vacuum System: Pumps and gauges create and maintain the vacuum environment.
-
Heating Elements: Typically made of graphite or molybdenum, these elements generate the heat for the process.
-
Cooling System: May include gas quenching or water cooling for rapid cooling of the workpiece.
-
Control System: Provides precise control over temperature, pressure, and time during the heat treatment process.
Advantages of Using Vacuum Heat Treatment Furnaces:
-
Reduced Oxidation and Decarburization: The absence of oxygen minimizes oxidation and prevents the loss of carbon from the workpiece surface, resulting in improved surface quality and mechanical properties.
-
Cleanliness: The vacuum environment eliminates contamination from atmospheric gases and dust, ensuring a clean and bright finish on treated parts.
-
Uniform Heating: The lack of air convection allows for more uniform heating, reducing distortion and improving consistency.
-
Enhanced Mechanical Properties: Vacuum heat treatment can significantly improve the strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance of materials.
-
Specialized Processes: Vacuum furnaces enable specialized processes like vacuum carburizing and nitriding, which are not possible in conventional furnaces.
Applications of Vacuum Heat Treatment Furnaces:
Vacuum heat treatment furnaces are widely used in various industries, including:
-
Aerospace: Heat treating critical components like turbine blades, landing gear, and engine parts.
-
Automotive: Hardening gears, shafts, and other engine and transmission components.
-
Medical: Manufacturing implants, surgical instruments, and other medical devices.
-
Tooling: Producing high-performance cutting tools, dies, and molds.
-
Electronics: Annealing semiconductor materials and other electronic components.
Types of Vacuum Heat Treatment Furnaces:
-
Single Chamber Furnaces: Basic design with one chamber for both heating and cooling.
-
Double Chamber Furnaces: Separate chambers for heating and cooling, improving efficiency and reducing cycle times.
-
Horizontal and Vertical Furnaces: Different orientations based on workpiece size and shape.
Choosing the Right Vacuum Heat Treatment Furnace:
Consider these factors when selecting a vacuum furnace:
-
Workpiece size and shape
-
Required temperature range
-
Cooling rate requirements
-
Production volume
-
Budget