How is Mineral Oil Produced?
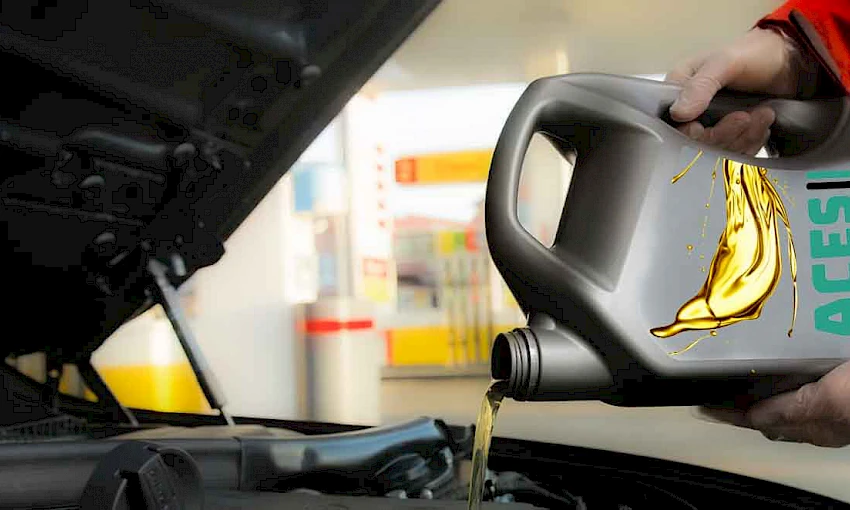
Mineral oil production is a complex refining process that yields a product used as a lubricant in engines and machinery. The process starts with crude oil and involves a series of steps, including distillation, hydrogenation, solvent extraction, and enrichment with additives. These additives provide essential physical and chemical properties, such as preventing wear, rust, foaming, and oxidation. Additionally, non-petroleum-based synthetic oils are often added to enhance the final product's chemical and physical properties.
Aces Process focuses on environmentally conscious and sustainable production methods in every stage of the mineral oil plants it installs. These efforts aim to minimize the environmental impact of industrial activities and leave a healthier planet for future generations.

Stages of Mineral Oil Production:
-
Crude Oil Extraction: Crude oil is transported to production facilities and stored in raw material stock tanks.
-
Crude Oil Refining: Crude oil is separated into different fractions with varying boiling points through processes like atmospheric and vacuum distillation.
-
Base Oil Production: Base oils, the foundation of mineral oil, are produced from the distilled fractions. These fractions undergo further processing, such as hydrogenation and solvent extraction, to improve purity.
-
Additive Blending: Additives are blended into the base oils to enhance their performance. These additives include detergents, antioxidants, anti-wear agents, viscosity modifiers, and anti-foam agents.
-
Blending: Base oils with different viscosities and properties are mixed with additives in specific ratios to achieve the desired characteristics of the final mineral oil product.
-
Filtration and Packaging: The final product is filtered to remove impurities and then packaged for distribution and use.
Important Processes in Mineral Oil Production:
-
Distillation: Separates crude oil into different fractions based on their boiling points.
-
Hydrogenation: Removes unwanted compounds like sulfur and nitrogen from base oils.
-
Solvent Extraction: Removes unwanted solvents from base oils through evaporation.
-
Additive Blending: Enhances the performance and properties of base oils.
-
Blending: Combines different base oils and additives to create the final mineral oil product.
-
Filtration: Removes impurities from the finished product.
-
Packaging: Prepares the mineral oil for sale and distribution.
Raw Materials Used in Mineral Oil Production:
-
Crude oil: The primary raw material.
-
Hydrogen gas: Used in the hydrogenation process.
-
Solvents: Used in the solvent extraction process.
-
Additives: Used to enhance the performance and properties of the mineral oil.
Main Types of Mineral Oils:
-
Automotive Oils:
-
Engine oils
-
Gear, bearing, and spindle oils
-
Transmission oils
-
Greases
-
Fully synthetic oils
-
-
Industrial Oils:
-
Heat treatment oils
-
Metalworking, leather, and textile processing oils
-
Hydraulic oils
-
Gear and slideway oils
-
Rust preventatives and solvent-based oils
-
Fully synthetic industrial oils
-
Environmental Impact of Mineral Oil Production:
Mineral oil production can pose environmental risks due to waste gases and wastewater generated during crude oil refining. Implementing measures to prevent pollution in production facilities is crucial.
Conclusion:
Mineral oil production is a complex process involving various steps and raw materials that directly influence the final product's properties and performance.
Additional Information:
-
Mineral oils are produced with different viscosities and properties to suit various applications.
-
In addition to their use as lubricants, mineral oils are also used in hydraulic fluids, metalworking fluids, and transformer oils.
-
Waste oils generated from the use of mineral oils can be recycled and reused.

If you need assist about your new plant installation progress, get in touch.
Writer:
Professor Doctor Mustafa Yaşar
Industrial Design Engineer