PROPERTIES OF ACIDS AND BASES
In this article, we will discuss the properties of acids and bases. The Latin word acidus is derived from the verb acere, which means “to be sour, sharp, or pungent.” Acidus means “sour, acidic, or sharp-tasting,” and this is how it entered chemistry.
The best definition of acids and bases was provided by Swedish scientist Svante August Arrhenius. He defined acids and bases in his own theory, known as the Electrolytic Dissociation Theory, which he developed in 1887. Because it was insufficient in explaining the acidity and basicity of substances that do not contain (H+) and (OH-) in their structure, the Bronsted-Lowry Acid-Base Definition and Lewis Acid-Base Definitions were developed in later years. According to Arrhenius, substances that give (H3O+) or hydronium ions to water when dissolved in water are defined as acids, while those that give (OH-) hydroxyl ions are defined as bases. According to Arrhenius, the H+ ion has no electrons. Since it consists entirely of positive charge, it combines with the H2O molecule in aqueous solutions to form the (H3O+) ion, or hydronium.
For a substance to be called an acid or a base, its ionic solubility in water is the first requirement. Substances that dissolve molecularly in water cannot be acids or bases.
Properties of Acids
-
When dissolved in water, it releases H+ ions into the environment.
-
Their pH is less than 7.
-
Their POH values are greater than 7.
-
In aqueous solutions, their (H+) concentrations are greater than their (OH-) concentrations.
-
Acids turn blue litmus paper red.
-
They have a sour taste.
-
They are caustic, causing a burning sensation on open wounds and skin.
-
They are corrosive and irritating.
-
They undergo neutralization reactions with bases, forming salts and H2O.
-
When dissolved in water, their ionization percentage determines their strength. A 100% ionized acid is strong.
-
Their aqueous solutions are electrolytes (electricity-conducting substances) that conduct electric current.
-
Their ability to conduct electricity depends on their concentration and strength. Stronger acids conduct better.
-
Acids can react with carbonates. This reaction produces salt, water, and CO₂ gas.
PROPERTIES OF BASES
-
When dissolved in water, they release OH⁻ ions into the environment.
-
NaOH (in water) → Na⁺ (in water) + OH⁻ (in water)
-
Their pH is greater than 7.
-
Their POH is less than 7.
-
In aqueous solutions, the concentration of (OH⁻) ions is greater than that of (H+) ions.
-
Bases turn red litmus paper blue.
-
They taste bitter.
-
They are slippery and give a slippery feeling to the hand.
-
They are corrosive and irritating.
-
They react with acids to form neutralization reactions, producing salt and H₂O.
-
When dissolved in water, the percentage of ionization determines their strength. A base that ionizes 100% is strong.
-
Their aqueous solutions are electrolytes (electricity-conducting substances) that conduct electric current.
-
Their ability to conduct electricity depends on their concentration and strength. Stronger ones conduct better.
Not every compound containing H is an acid.
C₆H₁₂O₆ (s) → C₆H₁₂O₆ (aq)
C₂H₅OH (s) → C₂H₅OH (in water)
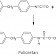
Not every compound containing OH is a base.
Alcohols → R–OH … (e.g., C₂H₅OH, CH₃OH)
They contain OH but are not bases.
Even if they contain OH⁻, they are not bases because they cannot form OH⁻ ions when dissolved in water.
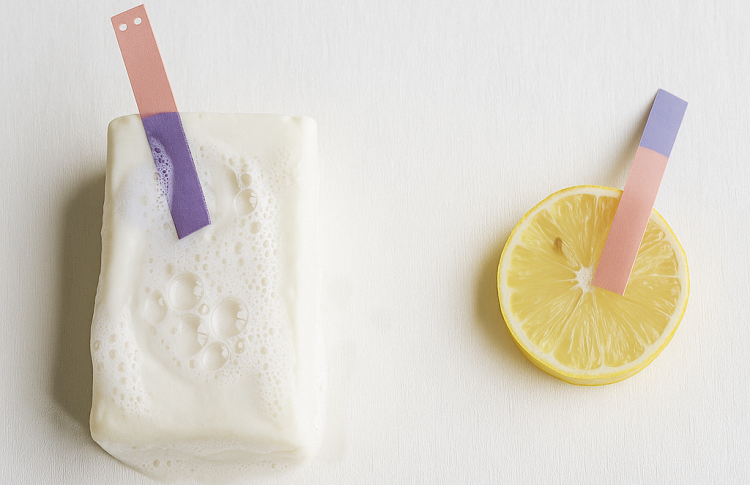

Indicator
Substances that help us determine whether a substance is acidic or basic, and if it is acidic or basic, how strong or weak it is, are called indicators.
|
Indicator - Acid Color - Base Color |
|
Litmus - Red - Blue |
|
Thymol Blue - Red - Yellow |
|
Bromophenol Blue - Yellow - Blue |
|
Congo Red - Blue - Red |
|
Methyl Orange - Red - Yellow |
Natural Indicators
|
Natural Indicators - Acid Color - Base Color |
|
Black Cabbage - Pink - Yellow |
|
Lavender- Colorless - Brown |
|
Rosehip - Red - Dark Green |
|
Cherry - Light Pink - Light Yellow |
|
Red Onions - Light Red - Light Brown |

Acids and Bases We Often Use in Everyday Life
Acetic Acid: It is the main component of vinegar (vinegar acid). It is used as a flavoring and preservative in foods.
Citric Acid: It is found naturally in citrus fruits such as lemons and oranges. It is used to add sourness and as a preservative in foods.
Sodium Bicarbonate: Known as “baking soda” or “baking powder.” It is used as a leavening agent, for heartburn relief, and in cleaning.
Sodium Hydroxide: Known as “caustic soda.” It is used in the manufacture of strong cleaning products such as soap, detergent, and drain cleaner.
Ammonia: A strong-smelling cleaning agent. It is used especially in glass cleaners and grease removers.
Hydrochloric Acid: Known as “Muriatic Acid.” It is a very strong acid and is used to clean tough surfaces such as toilets and bathrooms. It also aids digestion in our stomachs.
Writer:
Professor Doctor Mustafa Yaşar
Industrial Design Engineer