What are the Types of Flanges and How Many Types of Flanges are There?
In pipelines and equipment, robustness and leak-tightness are critical. This is where flanges come into play, enabling the safe and secure connection of pipes and equipment. So, what are flanges? How many types of flanges are there? When are they used? You can find the answers to all your questions about flanges in this article.
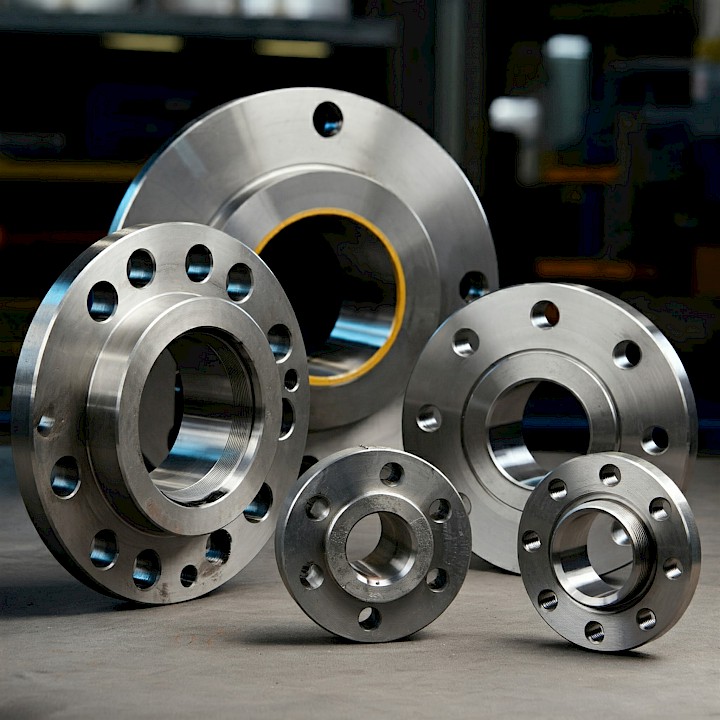

What is a Flange?
A flange is a connecting element typically used to join pipes or pipe sections or to secure equipment to a surface. Flanges, which consist of a metal disk, are equipped with holes and a connecting face. Bolts passing through these holes connect the flanges, creating a strong and leak-proof connection.
What are the Types of Flanges?
There are various types of flanges to meet different connection needs and applications. We can examine the most common types of flanges used in the industry under 8 main headings: flat flange, weld neck flange, threaded flange, loose flange, spectacle blind flange, lap joint flange, slip-on flange, and blind flange.
-
Flat Flanges: The simplest and most economical type of flange. Flat flanges are generally used in low-pressure applications.
-
Weld Neck Flanges: Flanges that are welded to the pipe. They are preferred in high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
-
Threaded Flanges: These flanges with threaded connections provide quick and easy installation. They are common in low-pressure applications.
-
Loose Flanges: Flanges that are connected with nuts and bolts without being welded to the pipe. They are easy to disassemble and provide flexibility.
-
Blind Flanges: Flanges used to close the end of a pipeline. Blind flanges are used for maintenance or repair operations.
-
Slip-On Flanges: Slip-on flanges are slid onto the outside of the pipe and secured with bolts. They are similar to flat flanges but offer easier and faster installation. They are common in low-pressure applications.
-
Lap Joint Flanges: Lap joint flanges are used to connect the ends of two pipes by overlapping them and securing them with bolts. They are similar to flat flanges but provide a more robust and leak-proof connection. They are preferred in high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
-
Spectacle Blind Flanges: Spectacle blind flanges consist of a ring that surrounds the pipe and is secured with bolts. These flanges allow connection without the need to drill the pipe, and a gasket is used for sealing. They are common in low-pressure and medium-pressure applications.
Applications of Flanges:
Flanges have a wide variety of uses in pipelines and equipment. Some of these are:
-
Water and gas pipelines
-
Oil and chemical transfer systems
-
Heating and cooling systems
-
Hydraulic and pneumatic systems
-
In machine and equipment connections
Flange Selection:
There are many factors to consider when choosing the right flange. The most important of these are:
-
Pressure and temperature: The flange to be used must be suitable for the pressure and temperature values in the system.
-
Pipe diameter: The flange should be selected in sizes appropriate to the diameter of the pipe.
-
Material: The flange material should be selected according to the type of liquid or gas in the system and the need for corrosion resistance.
-
Connection type: A choice must be made between different connection types such as flat, welded, threaded or loose flanges.
Advantages of Flanges:
Flanges are versatile fasteners that offer many advantages. Some of these advantages are:
-
Strong and leak-proof connections: Flanges provide leak-proof connections that are resistant to high pressures and temperatures.
-
Easy installation and removal: Properly installed flanges can be easily removed and reinstalled.
-
Flexibility: Different flange types and connection options adapt to different application needs.
-
Durability: Flanges are long-lasting and durable fasteners.


Writer:
Professor Doctor Mustafa Yaşar
Industrial Design Engineer