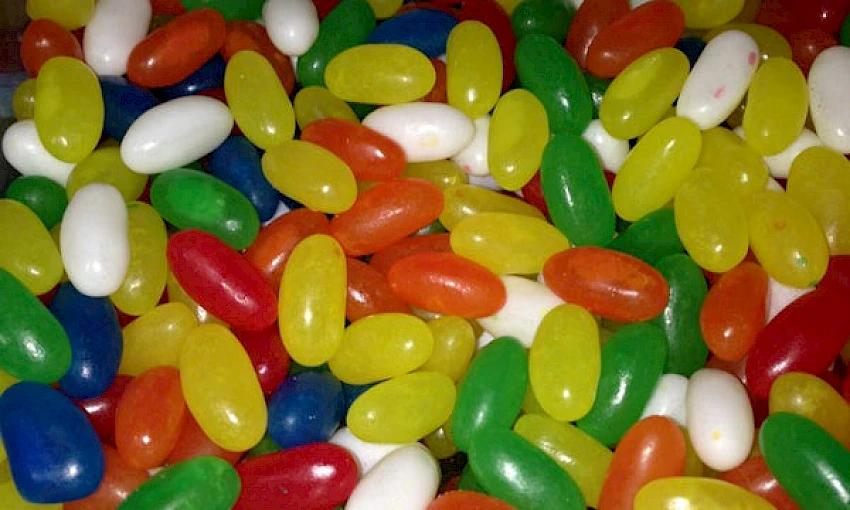
What is a Heterogeneous Mixture?
Heterogeneous mixtures are those where the components are not uniformly distributed, making them easily distinguishable to the naked eye or with optical instruments. These mixtures exhibit more than one phase, meaning that the different components retain their individual properties and do not fully blend together. Unlike homogeneous mixtures, heterogeneous mixtures do not have the same composition and density throughout.
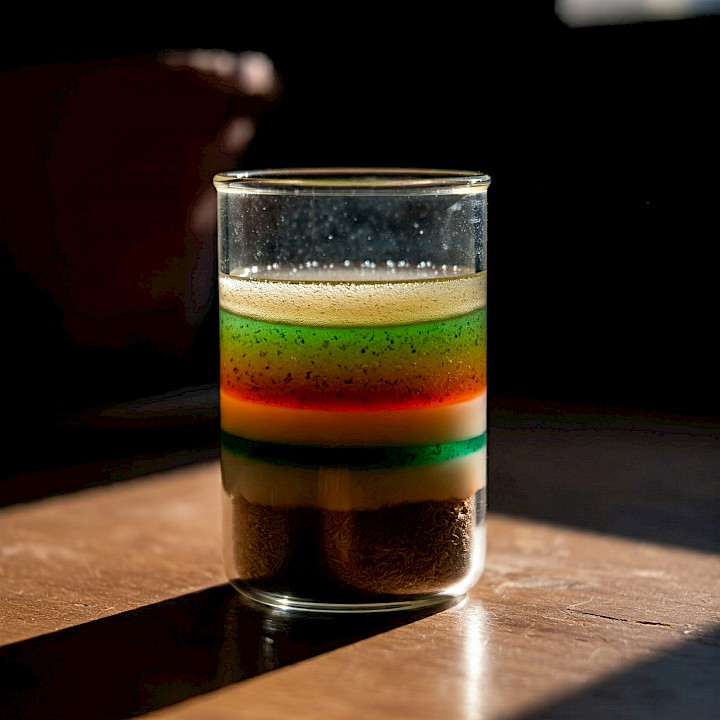

Characteristics of Heterogeneous Mixtures:
-
Visible phases: The different components are visibly distinct.
-
Non-uniform composition: The mixture does not have the same composition and density at every point.
-
Variable light transmission: Light may scatter or be blocked differently by the different phases.
-
Filterable: The components can often be separated by filtration.
Examples of Heterogeneous Mixtures in Industry:
Heterogeneous mixtures are commonly used in various industrial applications. Here are some examples:
-
Concrete:
-
Applications: Construction industry
-
Components: Cement, water, sand, and gravel
-
-
Asphalt:
-
Applications: Road construction and paving
-
Components: Bitumen and aggregates (sand, gravel, crushed stone)
-
-
Drilling Mud:
-
Applications: Oil and natural gas drilling
-
Components: Clay, water, chemicals, and additives
-
-
Slag for Steel Production:
-
Applications: Metallurgical industry
-
Components: Metal oxides and silicates
-
-
Paints:
-
Applications: Construction, automotive, furniture industries
-
Components: Pigments, binders, solvents, and additives
-
-
Pharmaceutical Suspensions:
-
Applications: Pharmaceutical industry
-
Components: Solid drug particles and liquid carriers
-
-
Cosmetic Products:
-
Applications: Personal care products
-
Components: Creams, lotions (oil and water phases), makeup (pigments and binders)
-
-
Agricultural Sprays:
-
Applications: Agricultural sector
-
Components: Pesticides, water, and carrier solvents
-
-
Mining Waste (Tailings):
-
Applications: Mining sector
-
Components: Various mineral particles and chemicals remaining after the extraction of valuable metals
-
-
Paper Pulp:
-
Applications: Paper industry
-
Components: Wood fiber, water, and various chemicals
-
Industrial Applications of Heterogeneous Mixtures:
Heterogeneous mixtures, composed of distinct phases, are widely used in various industrial processes:
-
Construction Materials:
-
Concrete: A mixture of cement, sand, water, and aggregates, forming a strong and durable construction material.
-
Asphalt: A mixture of bitumen, sand, and aggregates used for road surfaces and pavements.
-
-
Mining:
-
Ore: Contains valuable minerals along with rock and other minerals.
-
Sand and Gravel: Mixtures of sand grains and rock fragments of varying sizes.
-
-
Chemical Industry:
-
Catalysts: Heterogeneous mixtures used to increase the rate and efficiency of chemical reactions.
-
Adsorbents: Used to remove pollutants from liquids or gases by attracting and holding them on their surface.
-
-
Food Industry:
-
Bread: A mixture of flour, water, yeast, and salt.
-
Cakes and Baked Goods: Mixtures of flour, sugar, eggs, butter, and other ingredients.
-
Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese are examples of emulsions, where fat droplets are dispersed in water.
-
-
Cosmetic Industry:
-
Toothpaste: A mixture of abrasives, humectants, sweeteners, and flavorings.
-
Body Lotions: Mixtures of oils, water, moisturizers, and active ingredients.
-
Makeup Products: Mixtures of pigments, oils, binders, and other components.
-
Separation of Heterogeneous Mixtures:
Various methods are used to separate heterogeneous mixtures:
-
Sieving: Used to separate solid particles of different sizes.
-
Filtration: Used to separate solid particles from a liquid.
-
Centrifugation: Used to separate solid particles from a liquid based on density differences.
-
Evaporation: Used to obtain a solid residue by evaporating the liquid.
-
Distillation: Used to separate liquids with different boiling points.
-
Dialysis: Used to separate substances based on their molecular size.
-
Flotation: Used to separate solids in a liquid based on their densities.
Types of Heterogeneous Mixtures by Concentration:
-
Suspensions: Solid particles dispersed in a liquid, e.g., muddy water, paint, sand in water.
-
Emulsions: One liquid dispersed in another liquid, e.g., milk, mayonnaise, cream.
Writer:
Professor Doctor Mustafa Yaşar
Industrial Design Engineer