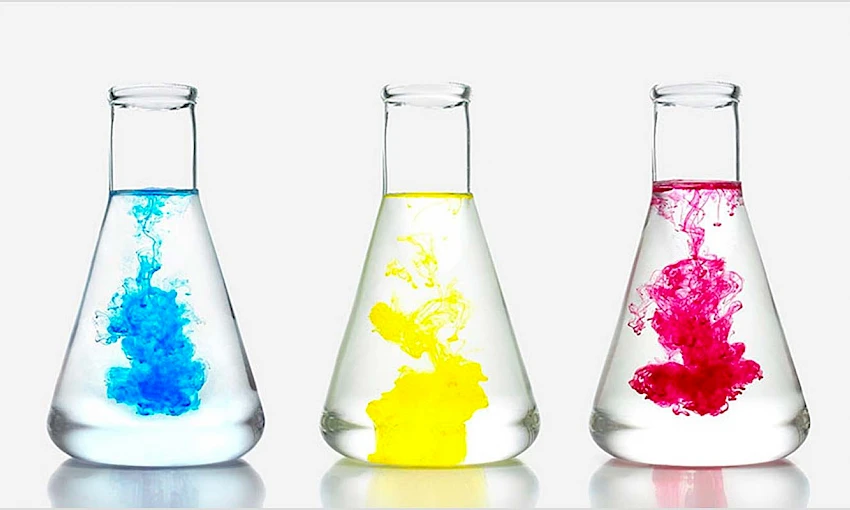
What is a Homogeneous Mixture?
Homogeneous mixtures are those where the components are uniformly distributed, making them indistinguishable to the naked eye or even with optical instruments. They appear as a single, uniform phase. In such mixtures, every point has the same properties and composition, and the dispersed substances have the same concentration throughout the mixture.

Characteristics of Homogeneous Mixtures:
-
Uniform composition and density: Any sample taken from the mixture will have the same composition and density.
-
Invisible components: Individual components cannot be seen with the naked eye or optical instruments.
-
Single-phase appearance: The mixture appears as a single, uniform phase.
-
Often referred to as solutions: Homogeneous mixtures are commonly called solutions.
-
Separable by specific methods: Homogeneous mixtures can be separated using techniques like filtration, centrifugation, or evaporation.
Examples of Homogeneous Mixtures:
-
Saltwater
-
Sugar water
-
Air
-
Alcohol
-
Vinegar
-
Metal alloys
-
Glass
Industrial Applications of Homogeneous Mixtures:
-
Food Industry: Homogeneous mixtures ensure uniform texture and extended shelf life in food products. Examples include fruit juices, sauces, mayonnaise, and ice cream.
-
Pharmaceutical Industry: Homogeneous mixtures are crucial for the safe and effective production of medicines, ensuring the even distribution of active ingredients for the desired therapeutic effect.
-
Chemical Industry: Homogeneous mixtures are used in the production and processing of various chemical products and raw materials, such as paints, varnishes, detergents, and fertilizers.
-
Cosmetic Industry: Homogeneous mixtures ensure uniform texture and easy absorption in cosmetic products like creams, lotions, foundations, and masks.
-
Mining Industry: Homogeneous mixtures are used to separate valuable metals and minerals from ores, such as in the flotation method.
Types of Homogeneous Mixtures by Size:
-
True solutions: Particle size of components is less than 1 nanometer (nm), e.g., saltwater, sugar water.
-
Colloids: Particle size of components is between 1 nm and 1000 nm, e.g., fog, smoke.
-
Suspensions: Particle size of components is greater than 1000 nm, e.g., muddy water, flour in water.
Types of Homogeneous Mixtures by Concentration:
-
Dilute solutions: Low concentration of solute, e.g., lemonade.
-
Concentrated solutions: High concentration of solute, e.g., seawater.
Separation of Homogeneous Mixtures:
-
Filtration: Used to separate solid and liquid phases.
-
Centrifugation: Used to separate liquid phases with different densities.
-
Evaporation: Used to separate a liquid phase from a solid phase.
Discover Our Industrial Mixers that Deliver Exceptional Performance in Homogeneous Mixtures!

Writer:
Professor Doctor Mustafa Yaşar
Industrial Design Engineer