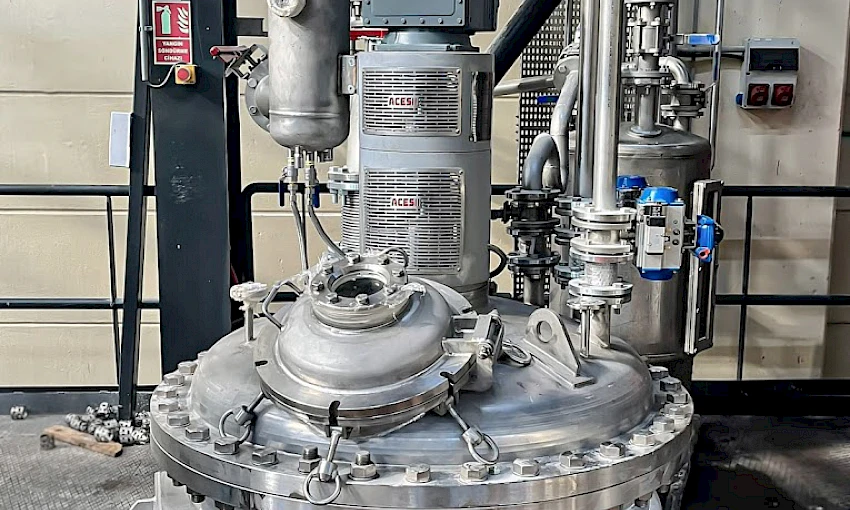
What is a Continuous Reactor?
Continuous reactors are closed systems where chemical and biological reactions occur seamlessly. Raw materials are continuously fed into the reactor, and products are continuously discharged, ensuring an uninterrupted production flow. These systems maximize efficiency in chemical production while minimizing waste generation. Their ability to operate for extended periods without interruption makes them a marvel of engineering.
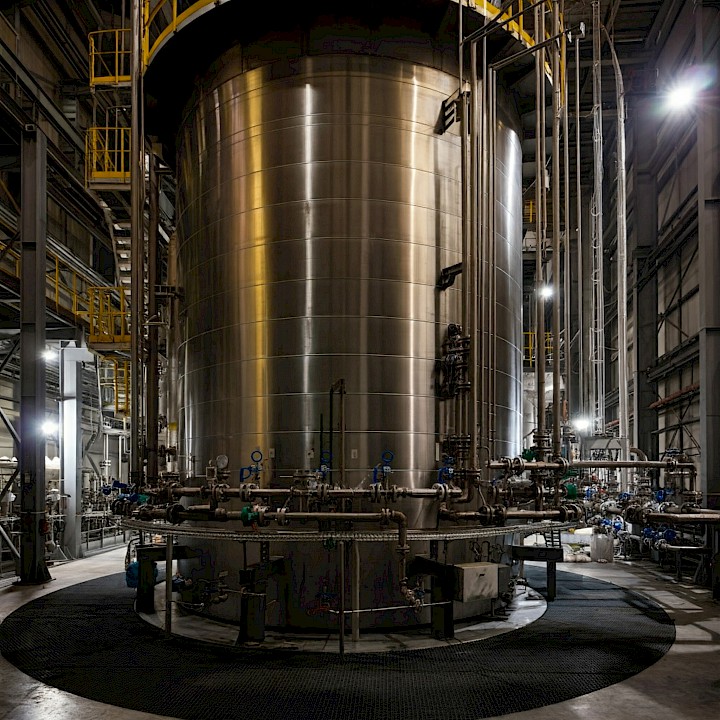

How Continuous Reactors Work:
-
Flow of Raw Materials: The reactor is continuously and precisely fed with raw materials.
-
Reaction: Chemical or biological reactions occur flawlessly within the reactor's specialized environment.
-
Discharge of Final Products: After the reactions are complete, the products are continuously discharged from the reactor.
-
Cycle: This seamless cycle continues without stopping, ensuring uninterrupted production.
Advantages of Continuous Reactors:
-
Efficiency: Optimal performance with full capacity utilization, minimal waste output, and maximum production.
-
Control: Reaction conditions are precisely controlled, ensuring consistently high product quality.
-
Production Performance: The reactors operate continuously, minimizing downtime and ensuring an uninterrupted production flow.
Disadvantages of Continuous Reactors:
-
Higher Setup Costs: The initial investment for continuous reactors is typically higher than for batch reactors.
-
Complex Operation: Flawless operation requires a complex design and meticulous management.
-
Limited Flexibility: Continuous reactors are not easily adaptable for producing different products; they are typically customized for a specific product.
Applications of Continuous Reactors:
-
Chemical Production: Used in the production of resins, fertilizers, plastics, and many other chemical products.
-
Refineries: Used to convert crude oil into gasoline, diesel, and other petroleum products.
-
Food Processing: Used for processing fruit juices, dairy products, and other food items.
-
Pharmaceutical Production: Used in the synthesis and production of pharmaceutical raw materials.
-
Biotechnology: Used in the production of enzymes and other biotechnological products.
Conclusion:
Continuous reactors have revolutionized chemical production, showcasing engineering ingenuity and innovation. They offer numerous advantages and specific applications. To understand the working principles and benefits of these systems, please contact us!

Writer:
Professor Doctor Mustafa Yaşar
Industrial Design Engineer