What is a Chemical Reaction?
A chemical reaction, in its simplest definition, is a process in which two or more substances interact, lose their original properties, and form new substances. The main reason for this is that atoms tend to achieve stability by reaching a noble gas electron configuration.
Example:
Sodium (Na) and Chlorine (Cl):
Na → Na⁺ + e⁻
Cl + e⁻ → Cl⁻
Sodium donates an electron, chlorine accepts an electron, and both become stable.
Chemical reactions form the basis of countless processes in the universe, from the shining of stars to digestion in the human body. But why do substances undergo change, and what happens during this process? Here is what you need to know about chemical reactions.
New Substances Do Not Exhibit the Properties of the Original Substances
- During a chemical reaction, electrons are transferred or shared between atoms.
- This leads to the formation of new bonds and the creation of completely different molecules or compounds.
- Since the internal structure of the new compound differs from that of the original substances, its physical and chemical properties are also different.
Electron Configuration and Chemical Properties
Electron configuration determines chemical properties because electrons control whether an atom will react, how it will bond, and which substances it will interact with.
Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
Exothermic Reactions
These reactions release heat to the surroundings. The temperature of the environment increases.
- CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O + heat
- 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O + heat
- C + O₂ → CO₂ + heat
- HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O + heat
- 2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO + heat
Endothermic Reactions
These reactions absorb heat from the surroundings. The environment becomes cooler.
- 2H₂O + heat → 2H₂ + O₂
- CaCO₃ + heat → CaO + CO₂
- 2KClO₃ + heat → 2KCl + 3O₂
- NH₄Cl + heat → NH₃ + HCl
- N₂ + O₂ + heat → 2NO
Polymerization Reactions
Polymerization is a reaction in which small molecules (monomers) bond together to form long-chain large molecules called polymers. Many everyday materials such as plastics, nylon, and rubber are produced through these reactions.
General representation:
n (monomer) → polymer
n CH₂=CH₂ → (–CH₂–CH₂–)ₙ (Polyethylene)
n CH₂=CHCl → (–CH₂–CHCl–)ₙ (PVC)
n CF₂=CF₂ → (–CF₂–CF₂–)ₙ (Teflon)
n CH₂=CH–CH₃ → (–CH₂–CH(CH₃)–)ₙ (Polypropylene)
Hydrolysis Reactions
A hydrolysis reaction is the breakdown of a compound into smaller molecules through reaction with water.
Characteristics of Hydrolysis Reactions
- Water is used
- Large molecule → smaller molecules
- Bonds are broken with the help of water
Protein + (n – 1) H₂O → n (Amino acids)
Carbohydrate + (n – 1) H₂O → n (Monosaccharides)
Fat + H₂O → Fatty acids + Glycerol
Sucrose + H₂O → Glucose + Fructose
Starch + n H₂O → n Glucose
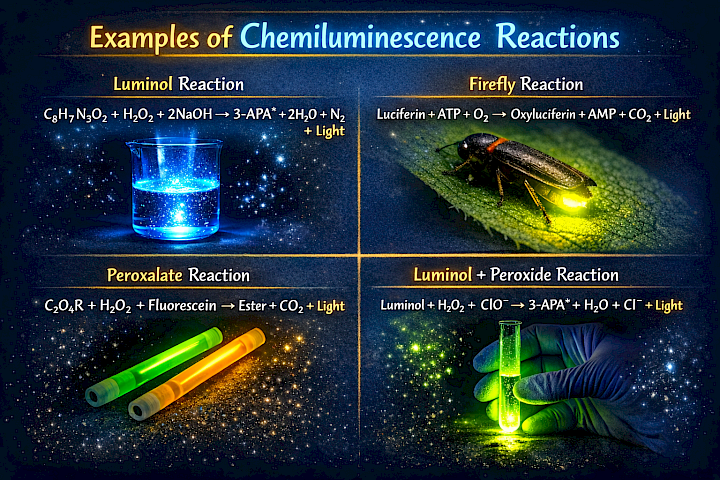
What Is Chemiluminescence?
Chemiluminescence is the emission of light during a chemical reaction. This phenomenon occurs as a result of changes in the energy levels of electrons within atoms. Because it is visually striking and useful for detecting certain substances, chemiluminescence is widely applied in scientific and analytical fields.
What Are the Types of Chemical Reactions?
Chemical reactions are processes that allow the formation of new substances by reorganizing matter at the atomic and molecular level. These reactions can be categorized based on their mechanisms and the way they occur. The most common types of chemical reactions are as follows:
-
Synthesis (Combination) Reactions
These are reactions in which two or more simple substances combine to form a more complex compound.
General equation: A + B → AB
Example: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O (Formation of water)
-
Decomposition (Analysis) Reactions
These are reactions in which a compound breaks down into simpler components or elements.
General equation: AB → A + B
Example: 2H₂O → 2H₂ + O₂ (Electrolysis of water)
-
Single Displacement (Single Replacement) Reactions
In these reactions, one element displaces another element in a compound.
General equation: A + BC → AC + B
Example: Zn + CuSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Cu (Zinc reacts with copper sulfate solution to release copper)
-
Double Displacement Reactions
In these reactions, ions of two compounds exchange places. These reactions usually result in the formation of a precipitate, gas, or neutralization.
General equation: AB + CD → AD + CB
Example: AgNO₃ + NaCl → AgCl (precipitate) + NaNO₃
-
Combustion Reactions
These are reactions in which a substance reacts with oxygen, releasing heat and light. Typically, the combustion of hydrocarbons and other organic compounds with oxygen produces water and carbon dioxide.
General equation: CₓHᵧ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O + Energy
Example: CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O + Heat (Combustion of methane gas)
-
Acid-Base (Neutralization) Reactions
In these reactions between acids and bases, a salt and water are usually formed.
General equation: Acid + Base → Salt + Water
Example: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
-
Precipitation (Sedimentation) Reactions
These are reactions in which ions in a solution combine to form an insoluble solid (precipitate).
Example: BaCl₂ + Na₂SO₄ → BaSO₄ (precipitate) + 2NaCl
-
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
These are reactions based on the exchange of electrons. Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons by an element, while reduction refers to the gain of electrons.
Example: Fe + O₂ → Fe₂O₃ (Rusting of iron)
Chemical reactions form the basis of many natural and industrial processes. Understanding these different types of reactions provides important applications in various fields, such as chemical engineering, environmental science, and biochemistry.
Discover the Power of Stainless Reactor Technology in Chemical Reaction Processes!
Writer:
Professor Doctor Mustafa Yaşar
Industrial Design Engineer